Information displayed
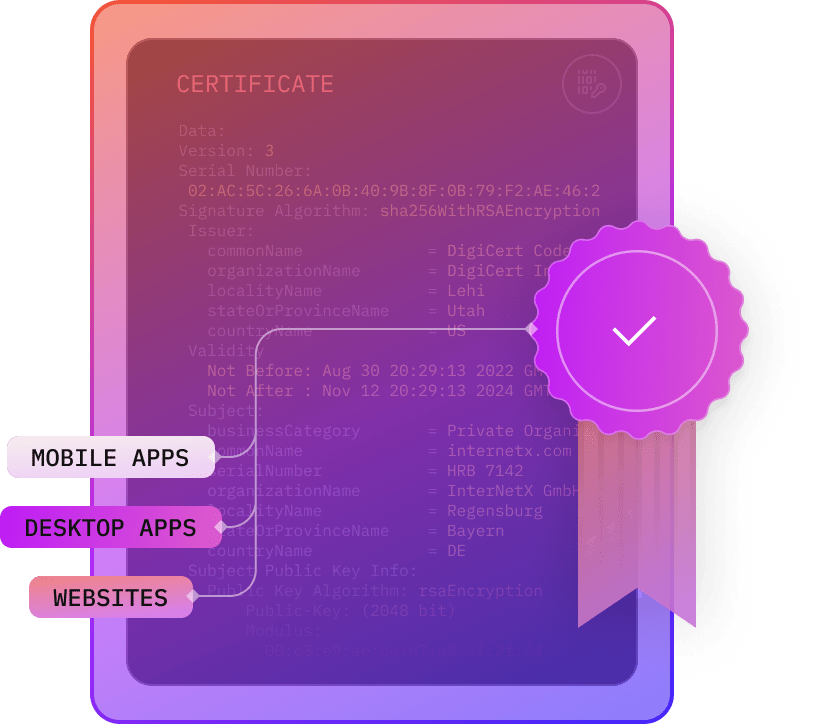
Code signing certificates improve UX and acceptance as they validate the origin and authenticity of software and applications. They show users that the installation of program codes is safe.
Public key infrastructure
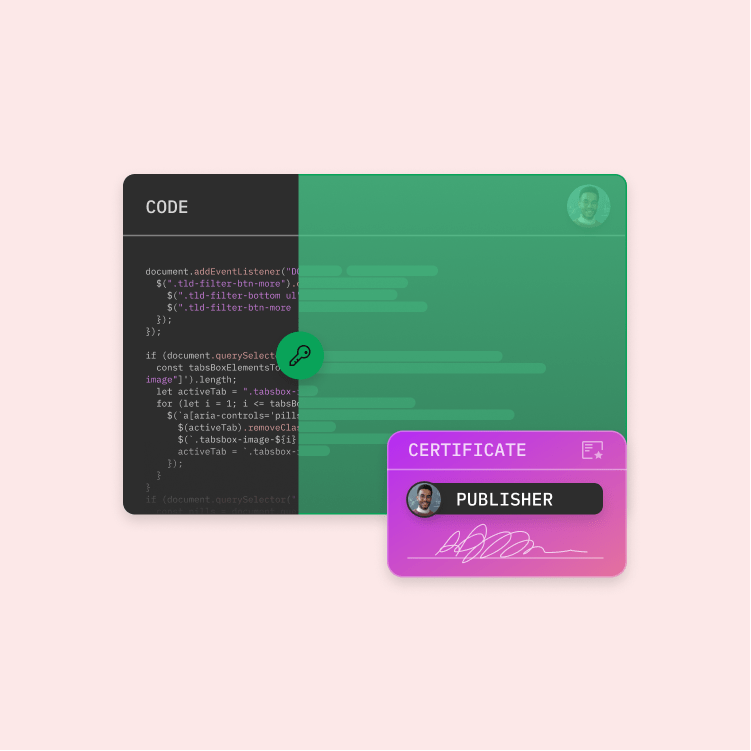
Digital signatures authenticate code by using public key encryption technology. The code is authenticated with a cryptographic key pair – a public and a private key. For this, code signing certificates use a cryptographic hash to guarantee the integrity of the code.
Hash function and private key
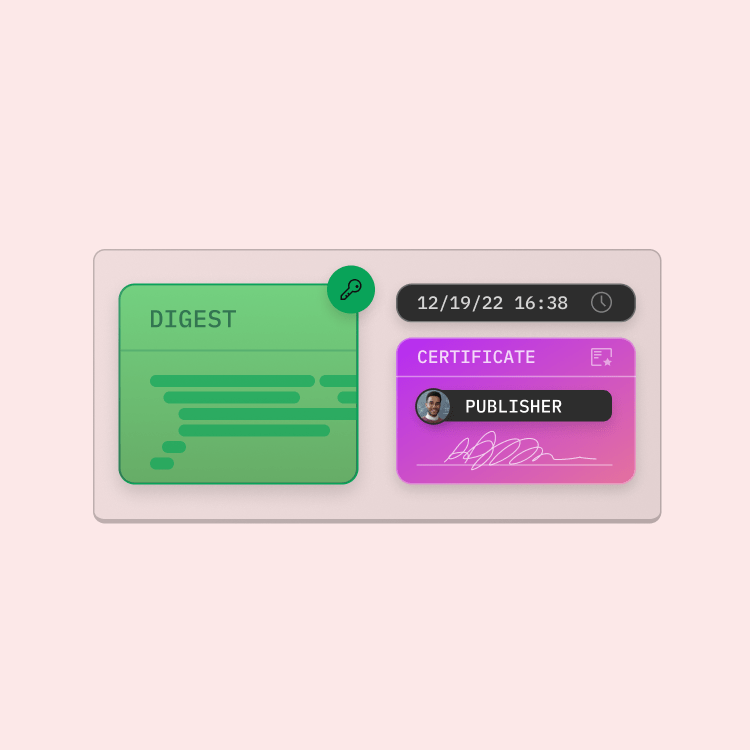
For the digital signature, the code must be hashed. The hash is a cryptographic representation of the file that can only be reproduced with the unmodified file and the hash algorithm that is used to create it. The output – the so-called digest – is then encrypted with a private key.
Code – signature – certificate
The digest and the code signing certificate are then combined into a digital signature block and a time stamp, if applicable, is added. The code signing certificate binds the identity of the company and the certificate authority to a public key that is always accessible and available for comparison.
Encryption of digital signature
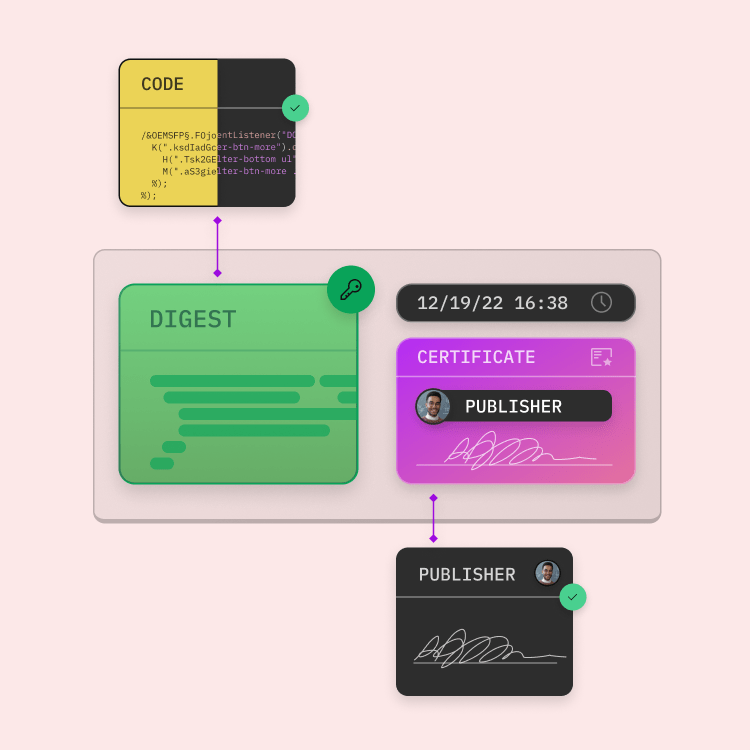
When the signed code is executed, the authenticity of the digital signature block is checked. Once this is confirmed, the digest is decrypted with the public key. The hash function is then applied to the software's code and the digest is matched with that of the author. If these match, the application is considered verified and safe to install.
Why you should use code signing certificates.
Two trends are driving the demand for code signing certificates. More and more software is entering the market. At the same time, malware is becoming a more frequent occurence. As software companies look for possibilities to guarantee the integrity of their products, code signing certificates offer a suitable means of providing protection and demonstrating security and authenticity to users.
DigiCert Code Signing (OV)
The DigiCert Code Signing certificate is used to sign software code, scripts and content, in order to authenticate the identity of the developer.
GlobalSign Code Signing
Applications digitally signed with a GlobalSign Code Signing certificate clearly identify the publisher and enhance user trust significantly.
| Features | Code signing (OV) | Code signing (EV) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Company name |
Company name |
|
Digital signature for unlimited applications |
|
|
|
Compatible with established platforms |
|
|
|
Immediate reputation with Microsoft Smartscreens |
|
|
|
Removes warning "Unknown publisher" |
|
|
|
Signature remains valid with use of timestamp |
Timestamp available |
Timestamp available |
Buy and manage code signing certificates.
In AutoDNS you gain access to a selection of code signing certificates from leading providers and for various applications. Use our domain and certificate platform to manage your certificate portfolio.
- TLS/SSL, S/MIME, VMC certificates
- Certificate wizard and CSR generator
- Advantages with Multi-year Plan
- API for easy implementation

Become a partner. With our SSL reseller program.
You are already an SSL reseller or would like to become one? You need a wide range of certifcates for your projects?
Benefit from our SSL reseller program. We offer excellent B2B conditions and a white-label SSL management platform with API access.
Our Partner Managers will work with you to draw up an individual reselling strategy for your business.
& conditions
FAQ.
Code signing protects both companies and users against damage due to software manipulation in executable files. The underlying process is based on the so-called public key infrastructure (PKI), which is also used for S/MIME or TLS/SSL certificates. It enables users to check the authenticity and validity of software before installation. By doing so, code signing certificates provide application security.
Thanks to the digital signature, users are able to make an informed decision about whether to execute the relevant software or file and can check its authenticity. As a rule, users should not trust unsigned code or applications as nobody can be held liable for any damages or errors in the application if the code has been manipulated by third parties.
Using code signing certificates, which are issued by independent certificate authorities like DigiCert, GlobalSign or Sectigo, the signature marks software applications with a "digital protection label" of sorts. This holds a number of competitive advantages:
- Software companies visibly communicate their identity.
- The integrity of digital products is guaranteed.
- Code signing ensures more application security and leads to higher company reputation amongst users.
There are two different types of code signing certificates offered by offical certificate authorities:
- Code signing certificates with organization validation (OV)
- Code signing certificates with extended validation (EV)
All types can be ordered and managed directly in AutoDNS.
The final price for a code signing certificate is determined by factors like:
- Provider
- Validity period (12, 24 or 36 months)
- Validation type (OV or EV)
You can find all available code signing certificates and prices in AutoDNS under > Security. You can also find an overview of all prices for our products under under > User management.
Every code signing certificate involves an identity check. Anyone who can prove their affiliation to a so-called "legal entity" (a registered company) or is a recognized software publisher can acquire code signing certificates as long as they meet the requirements for validation.
The delivery of code signing certificates depends on the certificate authority issuing the certificate.
- DigiCert delivers the certificates on a hardware token - optionally on a Digicert token (fee-based) or on a suitable hardware token provided by the certificate owner.
- Sectigo delivers the certificates on a hardware token - optionally on a Sectigo token (fee-based) or on a suitable hardware token provided by the certificate owner. The hardware token must verfiably originate from a specified provider.
- GlobalSign sends a free hardware token (once) which is included in the basic price. The hardware token cannot be cancelled.
Customs fees may apply for shipping.
Different application platforms support the signing of code and files and offer various tools and solutions.
Below you will find a list of the most common code signing types i.e. applications along with further information and instructions.
- Adobe Air
- Apple OS X
- Java
- Microsoft Authenticode Dateien in 32 bit and 64 bit user modus ..cab, .cat, . ctl., exe, .dll, .ocx, .msi, .xpi and .xap.
- Code for Microsoft Office
- Windows Makro and Visual Basic
- Mozilla & Netscape Objects
How to
- Digitally signing an AIR file
- Code signing guide by Apple
- Java code signing guide (DigiCert)
- Steps for the code signer (Oracle)
- How to sign applets using RSA-signed certificates (Oracle)
- XPI signing
- Code signing for VBA and Macros (GlobalSign)
- Signing and checking code with Authenticode
- Code signing best practises for the Microsoft Windows family of operating systems
Yes, in most cases. The warning is often generated by the Microsoft software called SmartScreen, which checks the reputation of a file i.e. software. A code signing certificate supports SmartScreen and helps it to determine whether a file or application is authenticated and safe. However, this cannot be guaranteed for all application cases.
Code signing certificates that are issued by public and independent certificate authorities (CAs) generate digital signatures that are recognized and classified as trustworthy by all standard operating systems and application platforms worldwide.
CAs like DigiCert, GlobalSign or Sectigo are subject to strict standards for issuing certificates and must undergo regular audits in order to guarantee compatibility with operating systems like or applications like Microsoft, Apple, Google or Mozilla.
With signed code, operating systems and applications check the issuing CA and the hash of the certificate used for the signature. If the CA is not included in the trusted list (root store) or if the hash is not identical, the signature is not trusted and the verification fails.
With private code signing, no such "seal" is added by a third and independent party. For this reason, we recommend acuiring a trusted code signing certificate for publishing and distributing software online so that the software application is labeled as safe to use.
Every code signature is generated on the basis of the content of the file that should be signed. The signing tool computes a compressed version of the file – the hash – and signs it using the relevant digital code signing certificate. The signed has is then embedded at a position in the code that is reserved for digital signatures.
As soon as the distribution of the signed file i.e. application or software is initiated, all standard operating systems as well as the relevant applications recognize the digital signature of the file. They automatically compute a hash of the file (without using the signed has in the computation) and compare it with the embedded signed hash. If these are identical, the validation is successful and the authenticity is verified. If the computed hash does not match the signed hash, the validation fails. A failed validation means that the content of the file has been changed after the file was digitally signed (whether due to error or due to malicious intent).
The reliability of this mechanism relies on the strength of the algorithm used for computing the hash – the longer the hash, the better. One of the standards most commonly used is SHA-256, an algorithm that generates a 256-bit hash.




![[Translate to Englisch:] ssl reseller [Translate to Englisch:] ssl reselling programm members](/fileadmin/files/ix/encryption/encryption-reseller-programm.png)