Profit from our DNS infrastructure services and enjoy maximum availability for your domains. With NodeSecure, zones are distributed around the world and are always available.
Virtual name servers
The use of our redundant name servers is free of charge for you if you register and manage domains with InterNetX. Domain resellers can also create their own virtual instances for customer projects in order to establish themselves as an independent provider in the DNS or WHOIS.
-
DNS infrastructure
-
Redundant name servers
-
Virtual instances
-
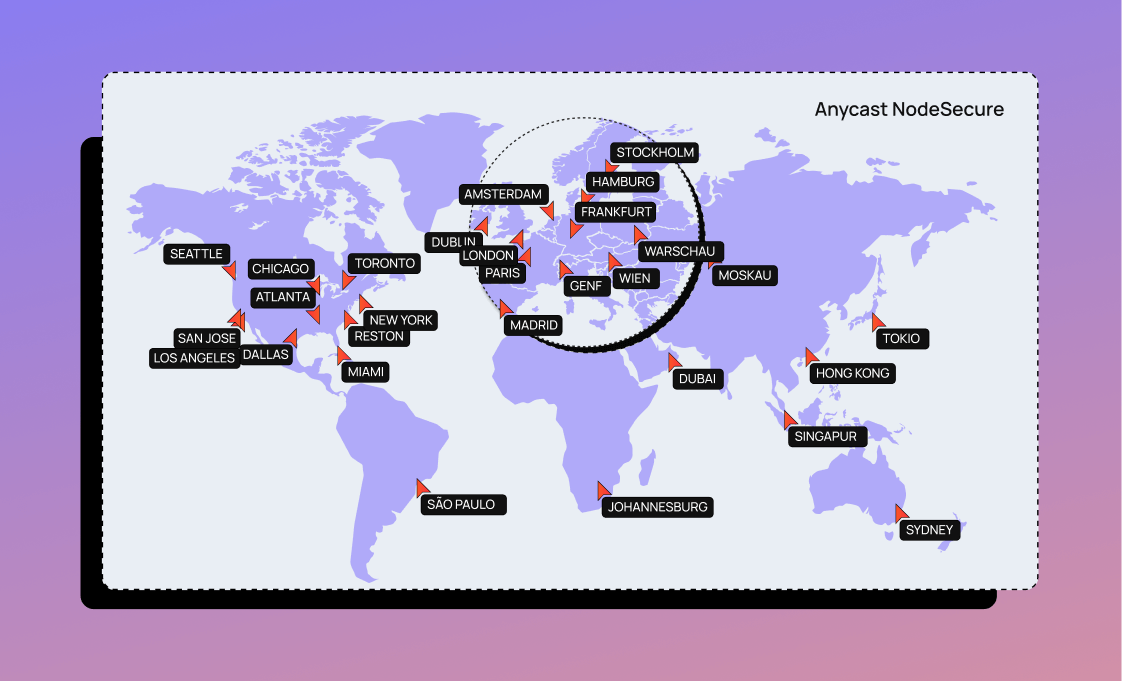
NodeSecure (Anycast service)
-
DNSSEC
-
API
DNS management with AutoDNS
With AutoDNS, you get a professional reseller admin panel for efficient management of your name servers and DNS zones. InterNetX provides all customers with a redundant nameserver infrastructure located at numerous locations in Europe and around the world. The utilization of InterNetX name servers is possible for all domain customers without any additional costs.

Virtual name servers are an important component of DNS and are used to resolve domain names into IP addresses. Unlike physical name servers, they are operated in virtualized environments, such as cloud platforms. Your business can profit from great advantages like scalability, resilience and easy management due to flexible resource allocation.

Dedicated name servers are physical servers that are used exclusively for DNS management. You get full control over the configuration and distribution of resources, which enables optimal performance and scalability. Enjoy higher security and lower risk of security breaches with dedicated name servers.


The NIS2 Directive aims to improve cyber security throughout the EU. It defines minimum requirements for security measures and reporting obligations for companies and operators of critical infrastructure.
As a domain registrar with a focus on meeting the highest security standards, we are fully compliant with the strict requirements of the NIS2 directive and ISO27001 certification.
This compliance ensures the highest level of protection for critical network infrastructures and services.
Future-proof infrastructure.
ISO 27001 certified.
ISO 27001 certification ensures a structured approach to information security management and therefore plays a crucial role with regard to NIS2. By implementing an information security management system (ISMS) in accordance with ISO 27001, InterNetX can identify, assess and control potential risks.
InterNetX manages the DNS infrastructure via a highly secure data center that meets the latest security requirements and is therefore ideally equipped for fulfilling NIS2 standards.
Unicast
Unicast is a classic routing scheme - also in the DNS. When users call up a website, there is a direct connection between the client and a server. Sending emails also usually works via unicast. With unicast DNS routing, the DNS resolver can retrieve a list of multiple DNS name servers, but it waits for the response or a timeout until it tries the next one. This can lead to high latency, especially when there are many simultaneous requests.
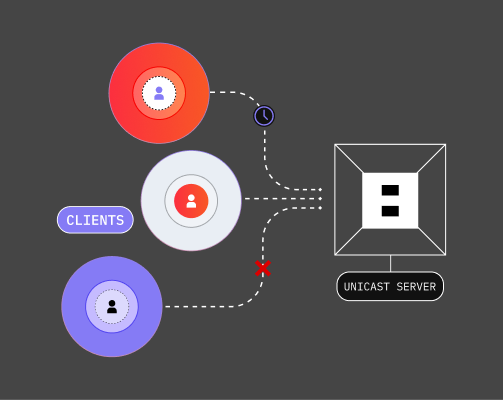
Anycast
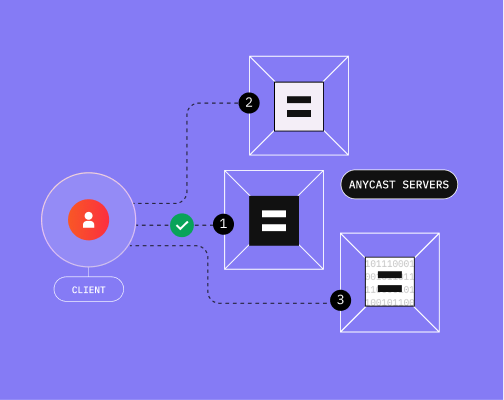
Anycast is a network routing method in which a client creates a connection to an address that is forwarded to one of several destinations. This allows the router to quickly select an optimal destination for the user and the provider.
In this way, the server availability can be established flexibly and optimized regardless of location.
Anycast is commonly used by content delivery networks (CDN) to effectively route users to points of presence (PoP). Anycast greatly maximizes availability, delivering a decisive advantage in the DNS.
FAQ.
The domain name system (DNS) does not contain a central database with all relevant information required for internet routing. This function is decentralized, undertaken and organized by umpteen thousand name servers. The DNS is based on a hierarchical information structure divided into different zones. The starting point for the data query is the so-called root directory. The domain information required for the addressing is queried at certain node points along a hierarchical system. The first layer of the hierarchy contains the root servers, followed by the name servers for the top-level domain (TLD) name servers and domain name system (DNS) name servers, which are managed by domain registrars such as InterNetX.
Domain customers and AutoDNS users can use the InterNetX name servers free of charge. In addition, domain resellers can set up and offer their own virtual name servers. Please contact us if you have any questions about this.
The domain name system (DNS) is based on network of name servers that allocate domain names to IP addresses. Name servers manage the necessary zone entries i.e. the resource entries (DNS records) which are central to the routing of data traffic in the internet by physically storing the zone entries. A virtual name server addresses another real name server and acts outwardly as an independent version of a name server in the DNS. However, the actual operation of the name server runs on the InterNetX servers.
An example:
ns1.internetx.com.de mirrors to ns1.your-domain.de
ns2.internetx.de mirrors to ns2.your-domain.de
You can set up and configure virtual name servers in AutoDNS.
Both elements – the name servers and the DNS zone entries – are fundamental to the routing of data for queries in the domain name system. The name servers i.e. the DNS servers are the physical storage locations of a DNS zone and provide these in the case of DNS queries. A DNS zone is a kind of “administrative conceptt” with which the central data is organized in the DNS. Each zone contains essential information about the operation of a domain, such as the IP address of the web server, the hostname of the mail server, additional subdomains, etc. These zone entries are saved on name servers i.e. the DNS servers and accessed there.
Whenever a user calls up a domain via a client, the client sends a DNS query to the name server and requests the zone entry A record or AAAA record, in which the information about the domain web server is saved. The name server responds to the browser with the saved IP address of the relevant server, allowing the browser to access the website and display the website content.
With every domain registration, registrants (private individuals or organizations) must specify name servers in order to enable access to the domain. If the zone entries have been stored correctly, the name servers then assign the correct IP address to a URL during client queries. Emails are assigned the correct mail servers in the same manner. A DNS server can be authoritative for several zones.
The following zone and resource entries are important for domain and DNS management:
- A – The A record points a domain to an IPv4 address
- AAAA – The AAAAA record points a domain to an IPv6 address
- ALIAS – The ALIAS record points to a hostname
- CNAME – The CNAME holds information about the hostname
- CAA – The CAA record holds information about the certificate authority that is authorized to issue certificates for the domain
- HINFO – The HINFO holds information about the host (processor type and operating system)
- MX – The MX record allocates a domain to a mail server
- NAPTR – The NAPTR record alloates a domain to a URI (uniform resource identifier)
- NS – The NS record identifies the authoritative DNS server for a domain
- PTR – The PTR record enables reverse lookup by showing which hostname belongs to a specific IP address
- SVR – The SVR record holds information about domain / subdomain services and is often used for XMPP, SIP or LDAP protocols
- TXT – The TXT record enables unstructured text to be saved
Name servers and the relevant zone entries for domains can be set up and managed efficiently in AutoDNS.
AutoDNS users can change the settings for each DNS entry – and even per record in the zone – to individually define the period for updates to become effective.
Yes, it is possible to transition your name servers to IPv6. However, this generally requires updates for both hardware and network infrastructure.
A primary DNS server contains all authoritative and relevant information for a domain, including the IP address and various other resource records. Primary name servers are also responsible for forwarding all relevant DNS entry updates or changes to the secondary DNS servers.
A secondary name server is a backup server that is set up to ensure that the domain remains available should the primary name server fail. Primary DNS severs therefore generally hold all the relevant resource records and process DNS queries for a domain. Secondary DNS servers hold read-only copies of zone files in order to provide relevant domain information if required.